| This is documentation for Semarchy xDI 5.3 or earlier, which is no longer supported. For more information, see our Global Support and Maintenance Policy. |
Getting Started with Spark
Prerequisites
The Hadoop Component must be installed.
Metadata creation
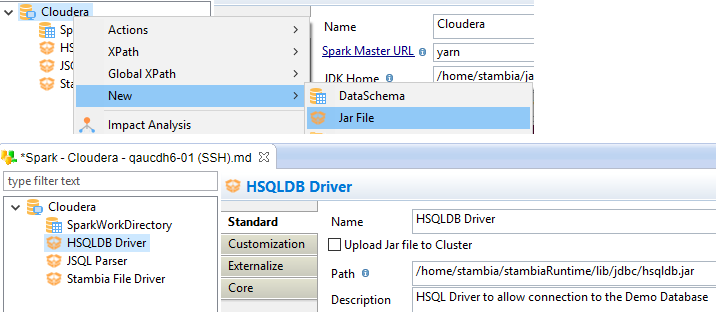
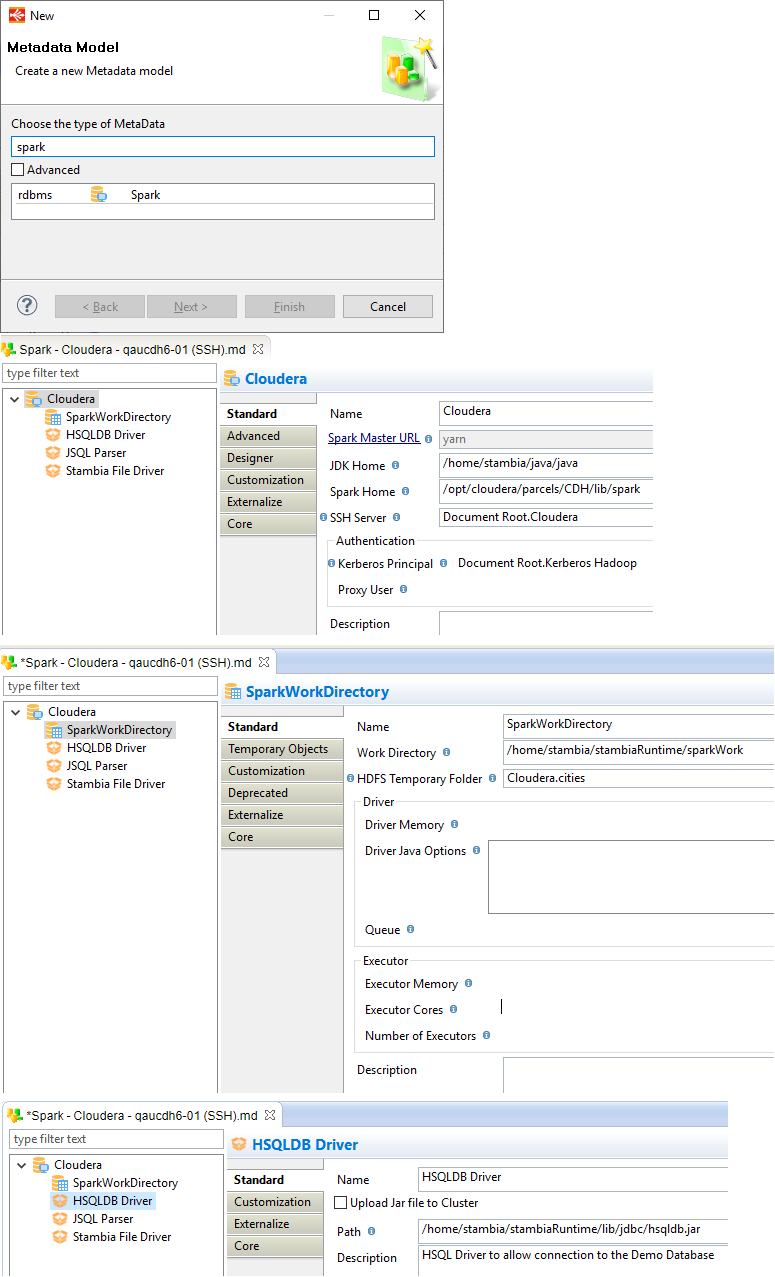
To start working with Spark in Semarchy xDI, the first step is to create the Spark Metadata.
Launch the Metadata creation wizard and create a Spark Metadata.
Below, a common example of a Spark Metadata.
Metadata configuration
This section explains how to configure Spark Metadata properly, according to your environments and requirements.
It describes also the existing properties for each node of the Spark Metadata.
Root node properties
The following properties are available on the Spark Metadata root node.
| Property | Mandatory | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Spark Master URL |
Yes |
Master URL used to connect to Spark |
spark://<host>:<port> |
JDK Home |
Yes |
Full path to a JDK that will be available on the server that compiles the classes. This will be used as follows: <JDK Home>/bin/javac |
/opt/java |
Spark Home |
Yes |
Home of the spark installation. This will be used to retrieve <Spark Home>/bin/spark-submit as well as <Spark Home>/jars/*.jar |
/opt/spark |
SSH Server |
No |
Drag and drop a SSH Server on this field when Spark cannot be accessed locally by the Runtime |
|
Kerberos Principal |
No |
Drag and drop a Kerberos Principal on this field when Spark installation is kerberized |
|
Proxy User |
No |
Spark proxy-user to use to impersonate the client connection. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
Schema node properties
The following properties are available on the Spark Metadata schema node.
| Some properties are available only for specific Spark Master URLs. |
| Property | Mandatory | Description | Example | Supported with Spark Master URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Work Directory |
Yes |
Full path to the directory in which the Runtime will compile the Jar files. When SSH is used, this must be a valid path on the SSH Server. |
/home/xdi/runtime/sparkWork |
all |
HDFS Temporary Folder |
No |
Drag and drop a HDFS Folder on this field. This will be used by some templates when needed to store temporary data in HDFS. This setting can be ignored if none of the templates require temporary HDFS data |
all |
|
Driver Memory |
No |
Amount of memory to allocate to the Spark Driver Program. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
2g |
all |
Driver Java Options |
No |
Specify any additional Java Options to pass when launching the driver program. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
--conf "spark.driver.extraJavaOptions=-Dlog4j.configuration=log4j.xml -Dconfig.file=app.conf" |
all |
Queue |
No |
Name of the Yarn queue to use when submitting the application. |
YARN only |
|
Executor Memory |
No |
Amount of memory to use per executor process. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
4g |
all |
Executor Cores |
No |
The number of cores to use on each executor. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
1 |
Spark Only |
Number of Executors |
No |
Number of executors requested to Yarn. |
1 |
YARN only |
Total Executor Cores |
No |
The total number of cores that Spark can use on the cluster. Please refer to the Spark documentation for more information. |
1 |
Mesos and Spark only |
JAR File node properties
The following properties are available on the Spark Metadata jar file node.
| Property | Mandatory | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Upload Jar file to Cluster |
No |
When SSH is used, this option allows to upload a local JAR File to the Cluster instead of referencing an already existing JAR File on this Cluster |
|
Path |
Yes |
Full Path to the Jar file on the Spark server |
/home/xdi/runtime/lib/jdbc/hsqldb.jar |
Tips and tricks
You can find below some of the main properties to have in mind for Spark Metadata.
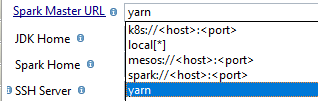
Spark Master URL
It defines how Semarchy xDI will connect to Spark.
You have many ways to set it: kubernates, local, yarn, spark, mesos, …
JDK and Spark Home
It defines the paths to corresponding directories, relative to the cluster you are working on.
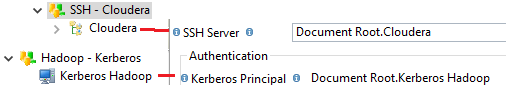
Related Metadata Links
Some properties require to select or drag and drop a Metadata Link.
This allows to define the connection properties to SSH, Kerberos, HDFS, and more…
Spark Properties
You can define other Spark properties, which correspond to the properties described in Spark Documentation.
Submit and Compilation Methods
There are two ways to submit Spark jobs in Semarchy xDI.
Both are using the "Spark submit" command to run jobs, but with difference regarding Java compilation.
Depending on your environment and preference, you can choose your preferred method.
Local method
With the local method, the Spark Java code generated by Semarchy xDI is compiled locally by the Runtime.
Then when the compilation is done, the generated JARs and dependencies are sent to Spark cluster and executed with the "Spark submit" command.
Below, an overview of this architecture.
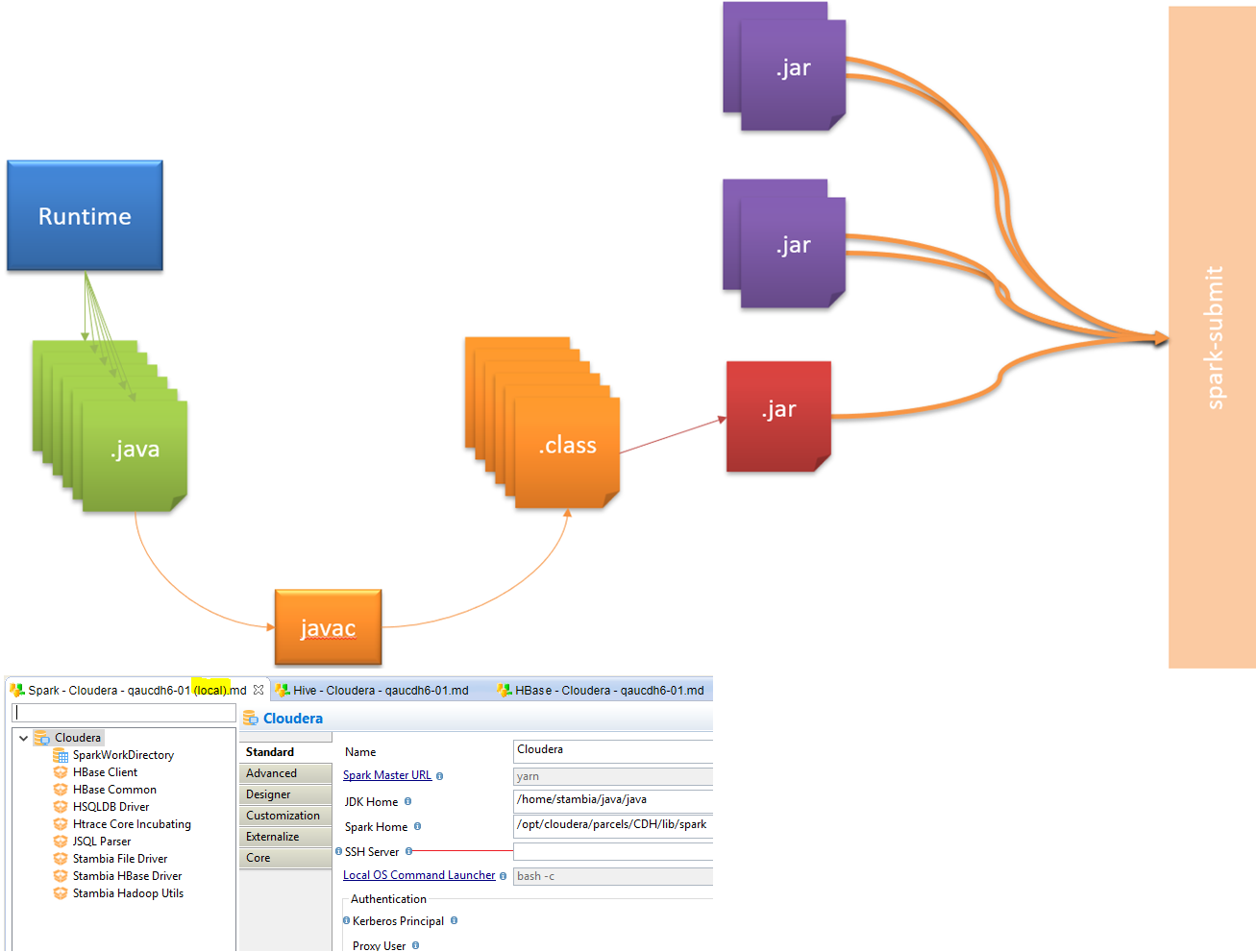
| Local method is the default method used, when no SSH Server is defined in Spark Metadata. |
Remote method (SSH)
With the remote method, the Spark Java code generated by Semarchy xDI is sent to Spark cluster with SSH.
Then, the Java code is compiled directly on Spark cluster, before being execute through "Spark submit" command.
Below, an overview of this architecture
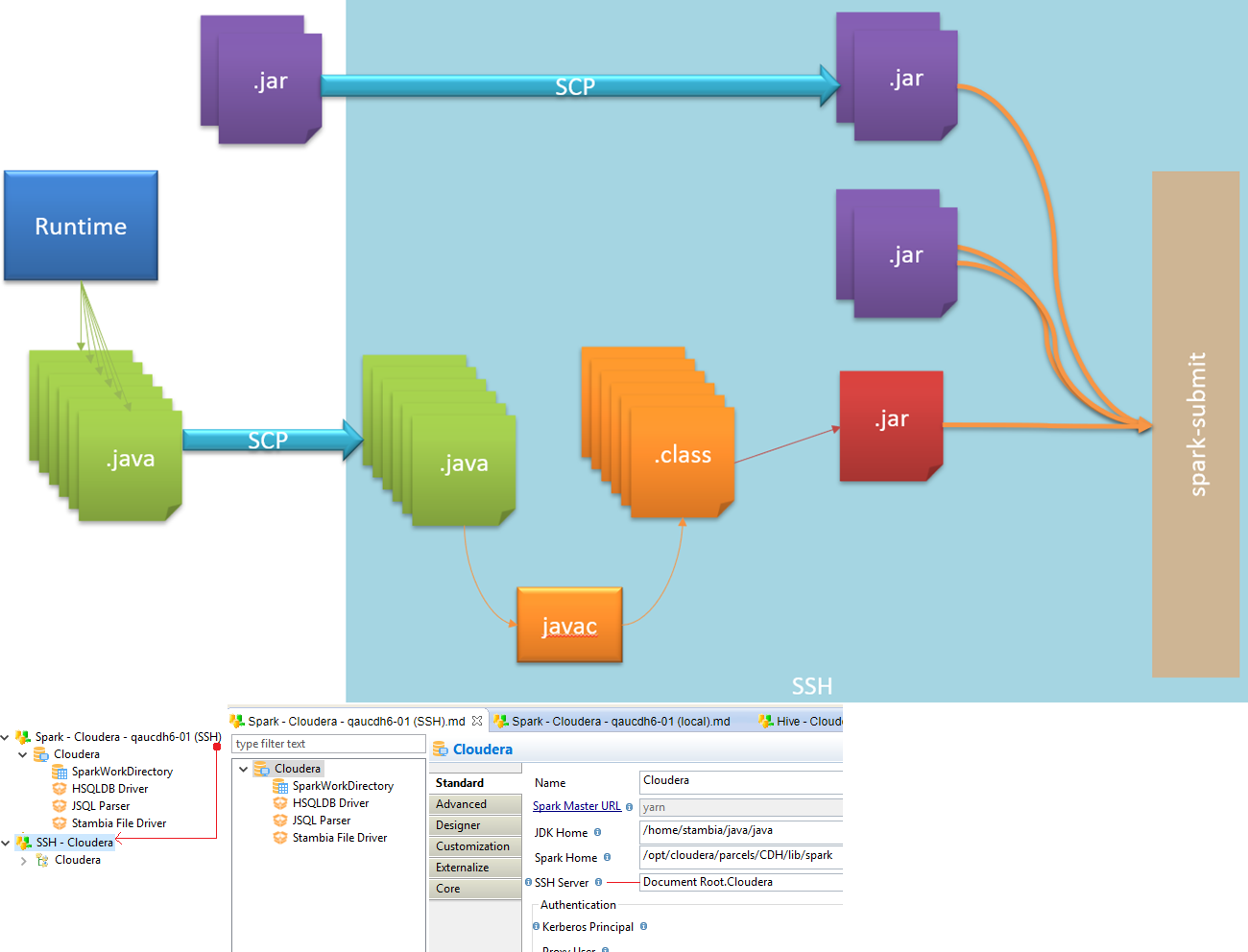
| To use the remote method, define an SSH Metadata Link in the Spark Metadata, in the corresponding property. |
Create your first Mappings
Spark can be used in many ways inside Semarchy xDI.
Spark Process Tools are available in the Process Palette, and Spark Templates in your Mappings.
Common Template Parameters
Below, a non-exhaustive list of common Spark Template parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Clean Temporary Objects |
If true, the temporary objects created during integration are removed at the end of the process. |
Coalesce Count |
If not empty, specifies the number of partitions resulting of a coalesce() operation on the Dataset. |
Compile |
When this option is set to true, the application is compiled and a JAR File is created. |
Debug |
When this option is set to true, additional information about the Datasets is written to the standard output. |
Execution Unit |
When multiple templates share the same Execution Unit name, only one of them will submit the JAR file embedding the Java programs for all other templates. |
Persist Storage Level |
Allows to select a persistence of the main Dataset. |
Repartition Count |
If not empty, specifies the number of partitions resulting of a repartition() operation on the main Dataset. |
Repartition Method |
Specifies how the data is to distributed |
Use Distinct |
If true, duplicate records will be filtered out. |
Submit |
When this option is set to true, the JAR file for this Execution Unit is executed using a spark-submit command. |
Work Folder |
Specify the location where the Java files are to be generated locally before being sent to the compile directory specified in the Spark metadata. |
Use Spark through Stages
The first way to use Spark in Semarchy xDI is through Mapping Stages.
You can drag and drop in a Mapping a Spark Metadata schema node and use it as a Mapping Stage.
Depending on your requirements and preference, you can use the stage to use Spark SQL expressions or Java expressions.
This is done by choosing the appropriate stage Template in your Mapping.
Spark SQL
Mapping stages using SQL expressions are common in Semarchy xDI.
To use Spark SQL, choose the appropriate Template and define your expressions.
Below, an example.
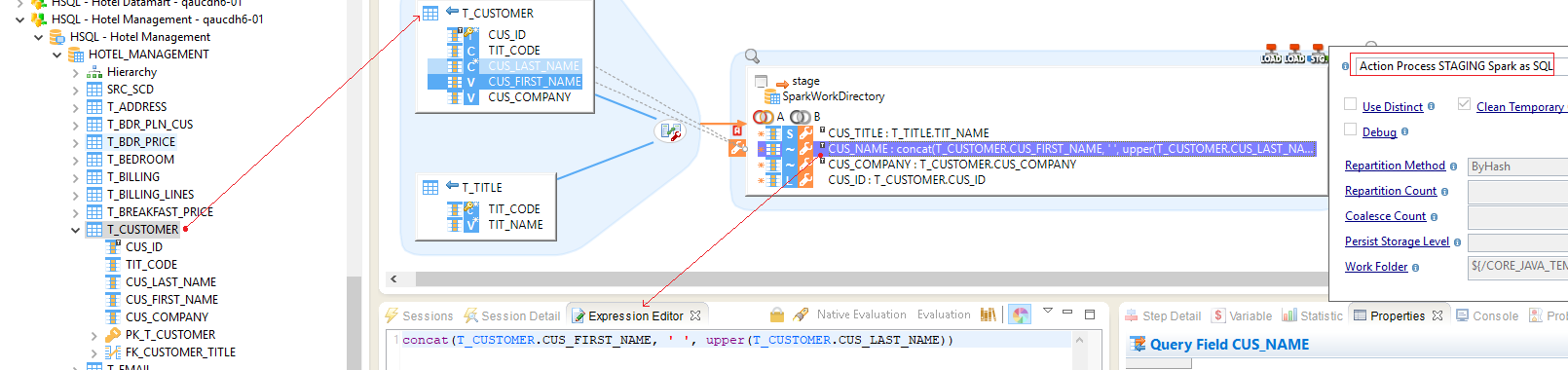
| On this example, there are two tables as source, and a Spark Stage configured with Spark SQL Template. The Template used is STAGING Spark as SQL |
Spark Java
To use Spark Java expressions, choose the appropriate Template and define your expressions as Java code.
Spark Map
The map Spark java mode means that every 1 line in source table, there will also be 1 line at staging (1-to-1 correspondence).
The code inside "Expression Editor" is written in Java.
Below, an example.
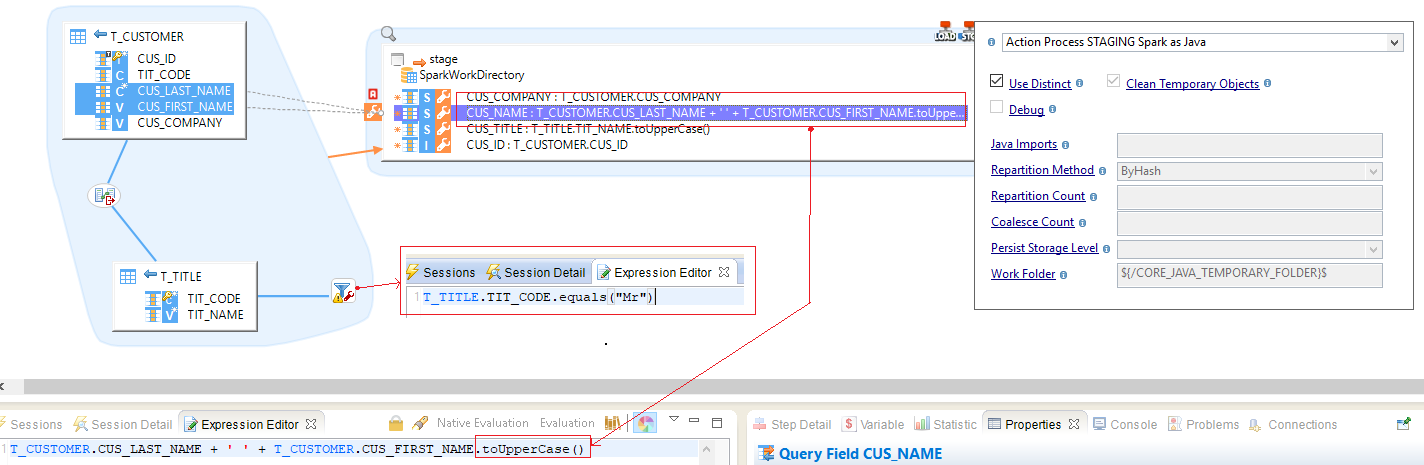
| On this example, there are two tables as source, and a Spark Stage configured with Spark Java Template. The Template used is STAGING Spark as Java |
| If you have only one line of Java code in the Expression Editor, you can omit the "return" key-word and the semicolon end instruction. |
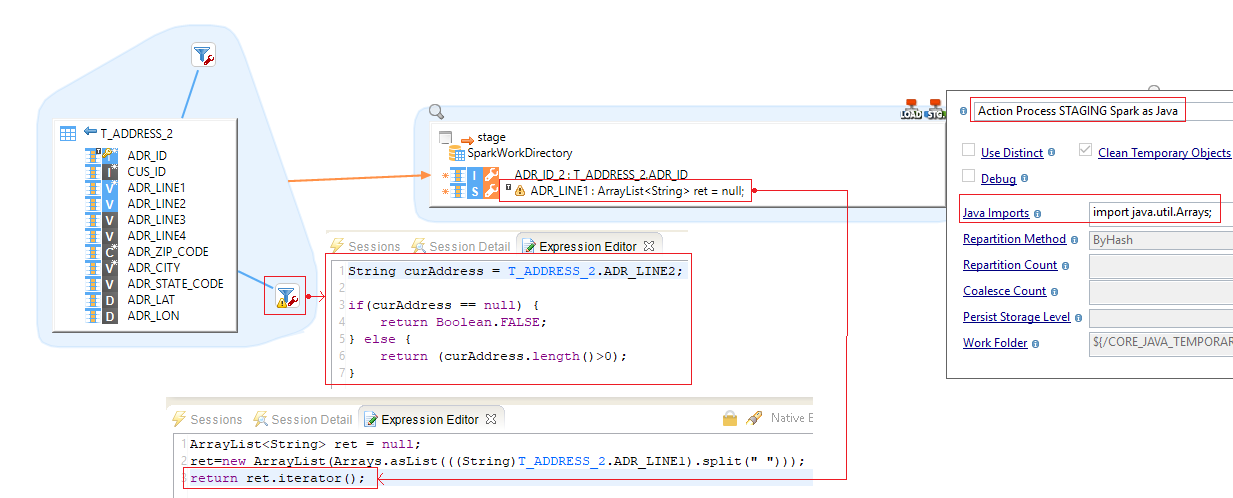
Flatmap
The Flatmap Spark java mode means that for every 1 line in source table, you can have many lines in staging step (1-to-N correspondence).
The code inside "Expression Editor" is written in Java.
| You have to return an "Iterator" interface in the mapping step. So you can use use your own objects if they implements the "Iterator" interface. |
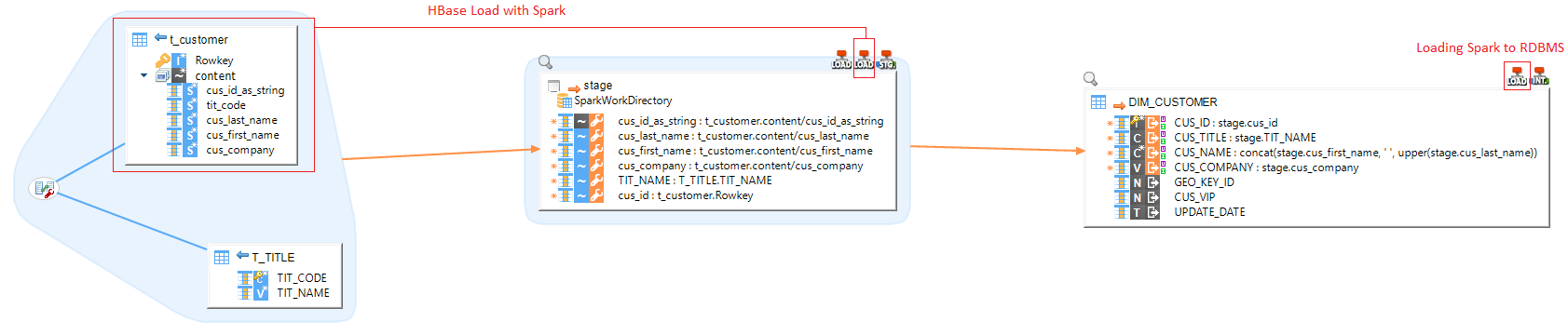
Manipulate data from remote technologies
Spark Component in Semarchy xDI allows to extract or send data from remote technologies through Spark.
You can manipulate data located in files, Hive, Hbase, and more… through Spark
To do this:
-
Create a Mapping
-
Define your remote source and target technologies
-
Provide a Spark Stage between them
-
Choose the appropriate Spark Template
Text files
In this example, we load two text files and merge them into one, through Spark.
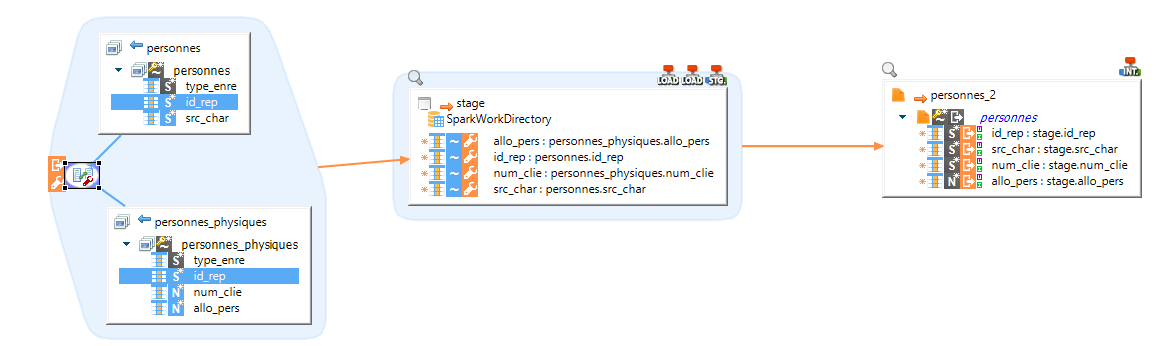
|
There are two source files, joined by a field. The final target is another file, which is supposed to contained both source file information |
Hive table
Hive as Source
In this example, we load an Hive table into an SQL table.
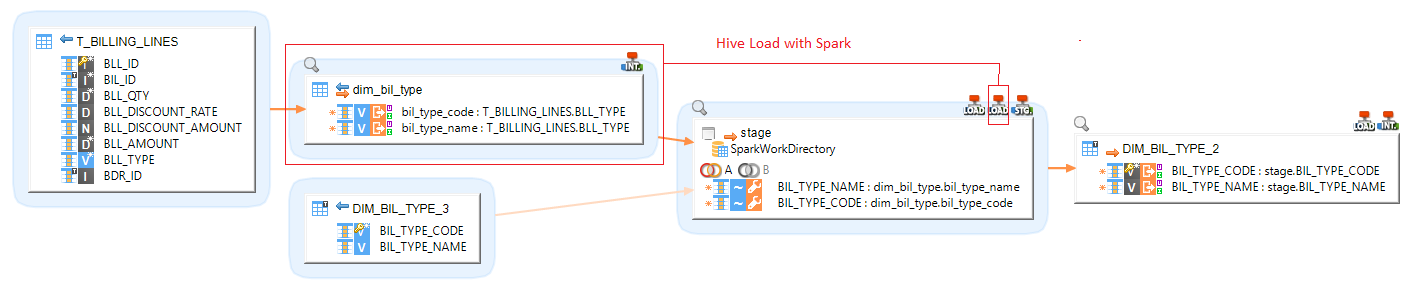
|
One of the sources is an Hive table: dim_bil_type. The final target table is an SQL table. |
Hive as Target
In this example, we load two SQL tables and merge them into an Hive table.
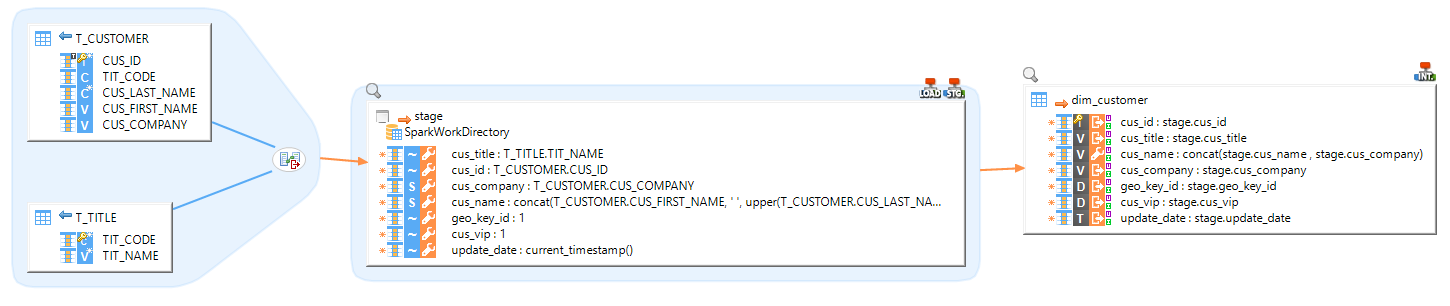
|
The sources are two SQL tables, joined by a column. The final target Target is an Hive table. |
| You can also load data to a more classical SQL (such as Oracle or Microsoft SQL Server) with the generic INTEGRATION Spark to Rdbms Template. |
Additional Notes
HDFS metadata links
Spark often works with HDFS data.
You can link files Metadata to an HDFS Metadata, as in the below example.
This indicates to Semarchy xDI that the files are in HDFS. Spark Templates will therefore automatically adapt.
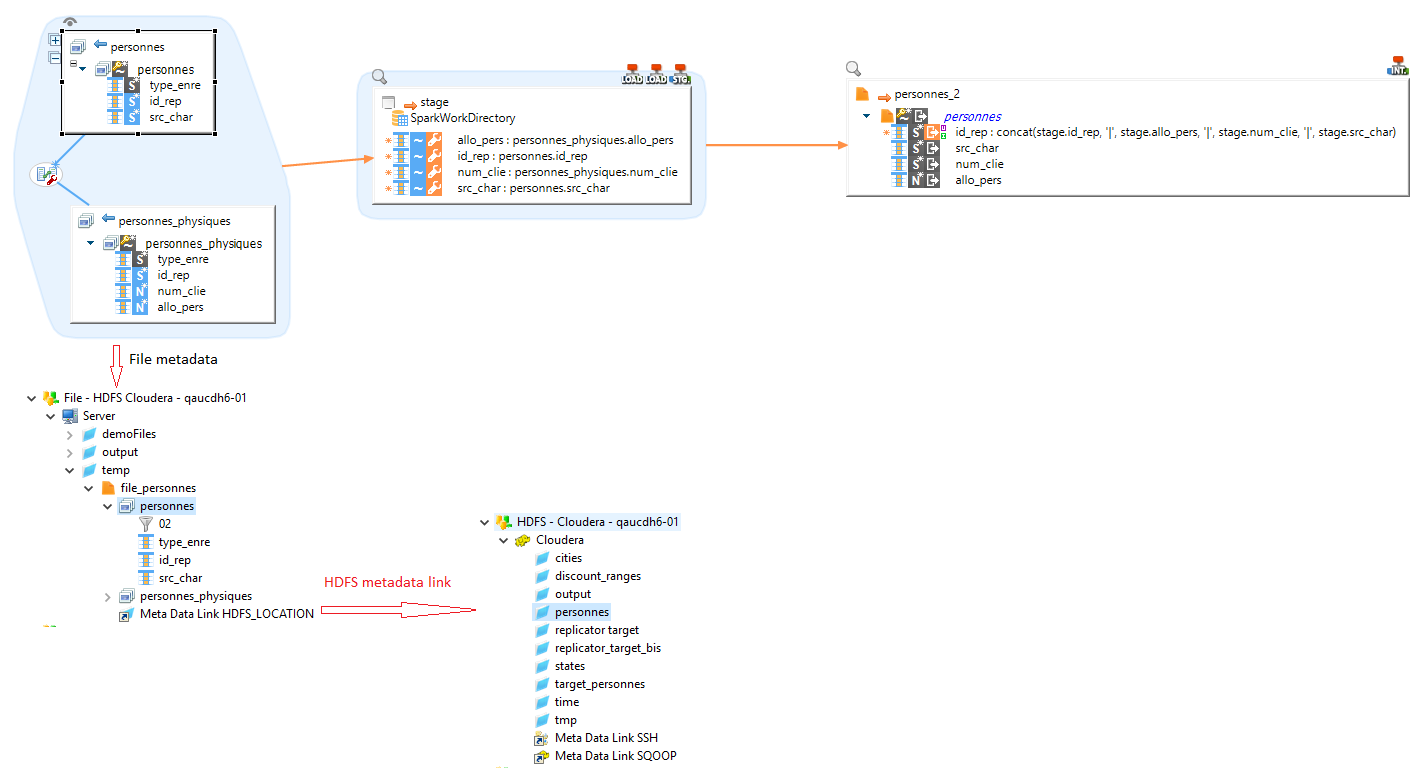
|
In this example, we use "personnes" file as source. |
| The Metadata Link must be named HDFS_LOCATION |